Virus-like particles (VLPs)
Virus-like particles (VLPs) consist of viral capsid proteins that assemble into macromolecular, particulate structures. Their repetitive and particulate structure stimulates the immune system similar to inactivated whole virus vaccines without the residual risk of infection in the latter. VLPs that present foreign antigens are called chimeric VLPs. This can be exploited, for example, in cancer immunotherapy, the immunotherapy of Alzheimer's disease and protection against infectious diseases. In addition to their immunological effect, VLPs have been used in some studies as targeted carrier structures for peptides, nucleic acids and drugs. The packaging of nucleic acids is of particular interest because of its proximity to the actual function of the viral capsid protein (which packages viral nucleic acids). Compared to monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), the processing of VLPs poses special challenges, e.g. because of their significantly larger geometry. At the chair we optimize the purification, processing and design of VLPs and genetic material. We use high-throughput methods, process analytical technology (PAT) and statistical methods such as machine learning.
Literature
Protein conjugation
The term protein conjugation describes the insertion of non-proteinogenic groups into protein molecules. The aim of this process is the production of molecules with unique properties. The covalent attachment of synthetic polymers to pharmaceutical proteins is a promising approach to alter physical properties such as thermal stability, solubility and tolerance to organic solvents. Furthermore, physiological properties like the half-life in circulation and the immune tolerance can be improved. The most common polymer modification in the pharmaceutical industry is the covalent attachment of polyethylene glycol (PEG) to the target molecule (PEGylation).
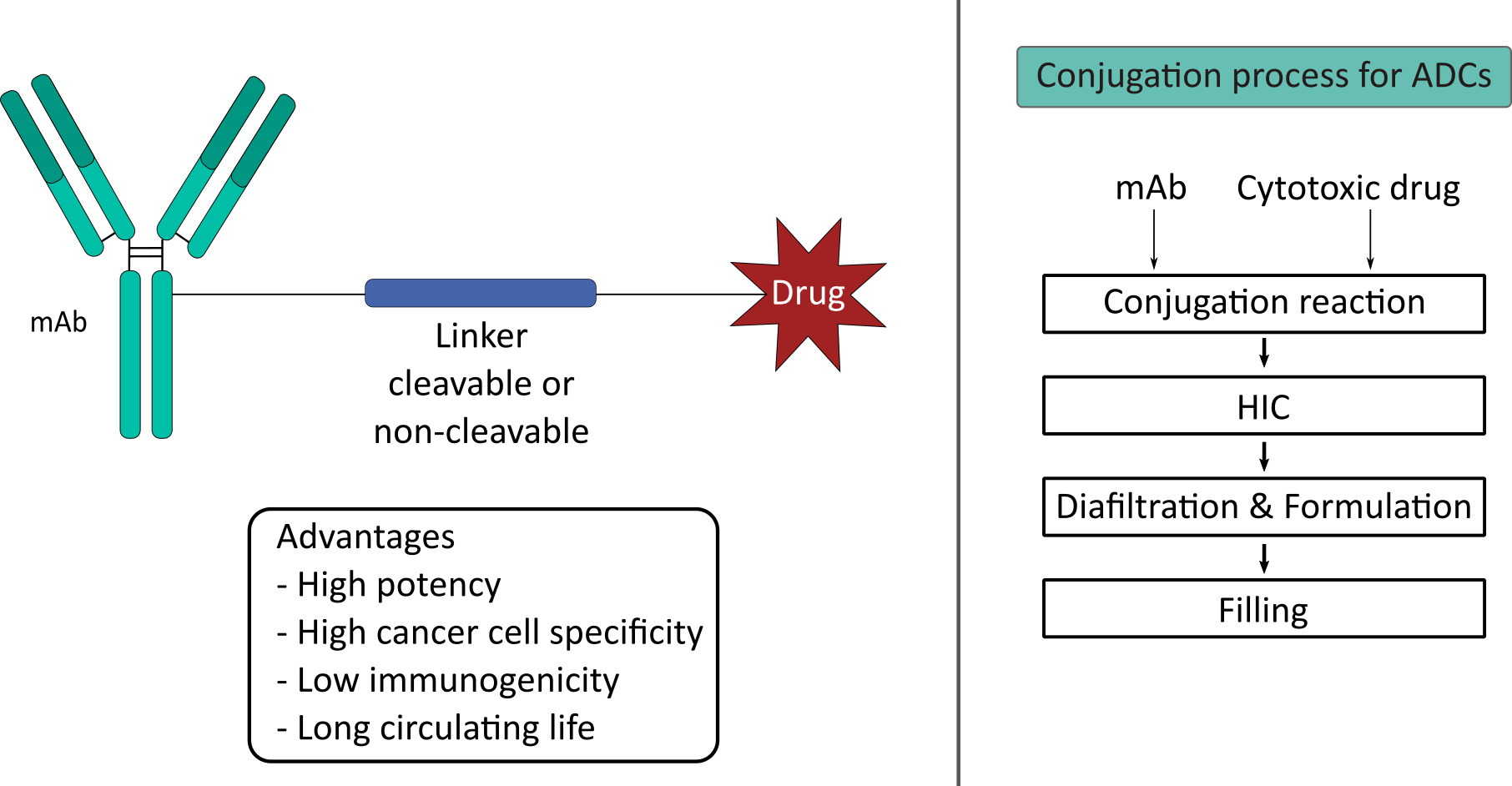
In cancer therapy the potential of antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) is made use of. In this case, biologically active cytotoxic drugs are coupled to monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) via a covalent linker. This way the specificity of the mAbs for antigens expressed on the cancer cells enables the targeted delivery of the cytotoxic payload mitigating the systemic effect of the drug. The bottleneck in the development of ADCs is the complex reaction kinetic and the purification. Therefore, our research focus lies in process development, control and also the application of digital tools.
Literature
Ultra-/Diafiltration
Ultrafiltration (UF) and diafiltration (DF) of biopharmaceutical protein solutions are standard unit operations for concentration and buffer exchange, respectively. We investigate processes that go beyond the usual size-dependent separation of the product from the surrounding liquid phase or impurities. Our research includes I) the product-specific development of process analytical technologies (PAT) including multiple sensors and custom-made software to enable real-time monitoring and control of UF/DF processes, II) the development of integrated processes by combination of UF/DF with other unit operations, such as precipitation/re-dissolution, size-exclusion chromatography, or biochemical reactions, and III) the development of experimental strategies for mechanistic modeling of UF/DF processes in co-operation with GoSilico GmbH.
Literatur
Crystallisation
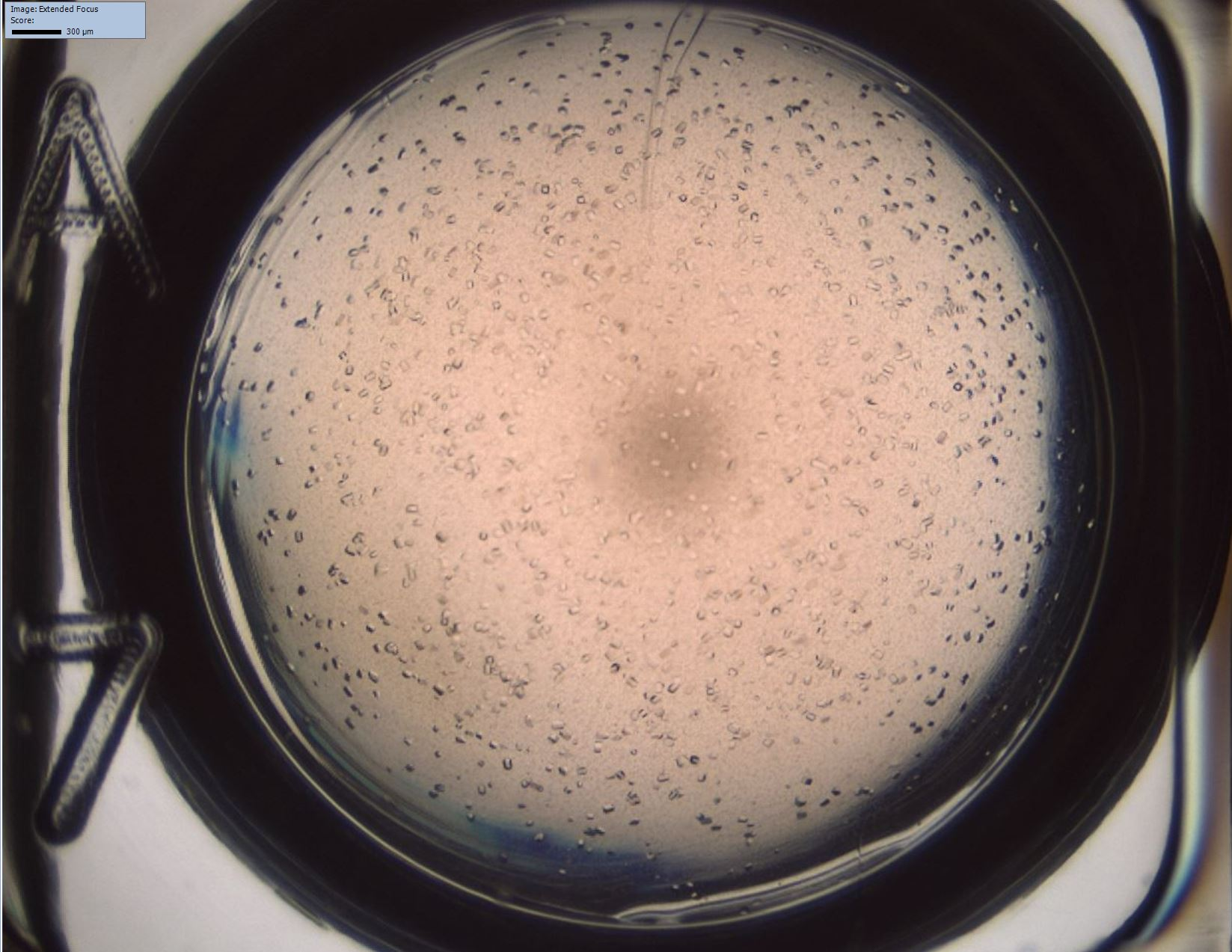
Crystallisation offers the biopharmaceutical industry an interesting, cost effective alternative to conventional separation and formulation methods. Due to the complex mechanisms during protein crystallisation optimal process conditions require empirical workflows. Undesired aggregation may lead to product loss and change in the three-dimensional structure of the target molecule. Therefore, knowledge of protein phase behaviour is essential for downstream process design.
At our institute screening methods are developed to generate phase diagrams in high throughput on an automated liquid handling station in microbatch scale. Automated supernatant measurements and sample imaging with a high-resolution camera provide information on the phase behaviour of the target protein in a complex protein mix to study the influence of process parameters, such as type and concentration of salts/polymers, temperature or pH.
Literature
Other topics
Automation and High-throughput process development (HTPD)
Literature
Chromatography
Literature